wellhealthorganic.com:health-hazards-of-prolonged-sitting
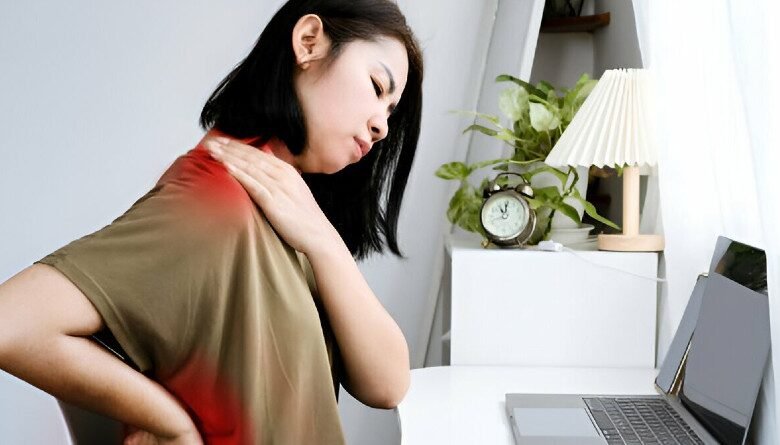

Prolonged sitting has become a common aspect of modern life, especially with the increasing prevalence of desk jobs, long commutes, and sedentary leisure activities. However, the health hazards associated with prolonged sitting are substantial and often overlooked. This article delves into these risks, drawing insights from wellhealthorganic.com , and provides practical tips for mitigating the adverse effects.
The Health Risks of Prolonged Sitting
Cardiovascular Disease
One of the most concerning health hazards of prolonged sitting is its link to cardiovascular disease. According to wellhealthorganic.com
, sitting for extended periods can lead to several adverse cardiovascular effects. Extended inactivity is associated with increased blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, excess abdominal fat, and unhealthy cholesterol levels. These factors collectively elevate the risk of heart disease and stroke. Research has demonstrated that people who sit for more than six hours a day have a higher risk of cardiovascular problems compared to those who are more active.
Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
Prolonged sitting significantly contributes to obesity and metabolic syndrome. wellhealthorganic.com
highlights that sedentary behavior reduces the body’s ability to burn calories, leading to weight gain. When physical activity is minimal, the body’s metabolism slows down, which can lead to fat accumulation. This inactivity is also linked to metabolic syndrome—a condition characterized by a combination of high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels. These conditions increase the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes and other chronic diseases.
Musculoskeletal Problems
The impact of prolonged sitting on the musculoskeletal system is another significant concern. wellhealthorganic.com
notes that sitting for long hours can result in poor posture, which places undue strain on the spine, neck, and shoulders. This strain can lead to chronic pain and discomfort and in severe cases, contribute to conditions such as herniated discs and muscle degeneration. Extended sitting can also weaken the muscles of the back and core, making it difficult to maintain proper posture and increasing the risk of musculoskeletal injuries.
Diabetes and Insulin Resistance
Another health risk associated with prolonged sitting is the development of type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. wellhealthorganic.com
points out that extended periods of inactivity can lead to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This resistance results in elevated blood sugar levels, which can eventually lead to type 2 diabetes. Research indicates that individuals who sit for long durations without regular physical activity have a higher risk of developing diabetes.
Mental Health Issues
In addition to physical health problems, prolonged sitting can negatively impact mental health. wellhealthorganic.com
highlights the link between sedentary behavior and increased levels of anxiety and depression. Physical inactivity is associated with reduced production of endorphins and other mood-enhancing chemicals, leading to feelings of anxiety and depression. The lack of physical activity can also contribute to poor sleep quality and overall reduced mental well-being.
Tips to Mitigate the Health Hazards of Prolonged Sitting
Incorporate Regular Movement
To counteract the effects of prolonged sitting, wellhealthorganic.com
suggests incorporating regular movement into your daily routine. Aim to stand up and move around for at least five minutes every hour. Simple activities like stretching, walking, or even doing a quick set of exercises can significantly improve circulation and reduce the risks associated with prolonged sitting.
Use Ergonomic Furniture
Investing in ergonomic furniture is another effective strategy. wellhealthorganic.com
recommends using ergonomic chairs and desks that support proper posture and reduce strain on the body. Adjustable desks that allow you to alternate between sitting and standing can also be beneficial, promoting movement and reducing the time spent in a static position.
Practice Good Posture
Maintaining good posture while sitting is crucial for preventing musculoskeletal issues. wellhealthorganic.com
advises keeping your feet flat on the floor, your back straight, and your shoulders relaxed. Your computer screen should be at eye level to avoid straining your neck. Regularly checking and correcting your posture can help alleviate discomfort and prevent long-term health problems.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is important for overall health and can also encourage more frequent movement. wellhealthorganic.com
notes that staying hydrated may prompt you to get up to refill your water bottle and use the restroom, which contributes to reducing sedentary time.
Incorporate Physical Activity into Your Day
Regular physical activity is essential for mitigating the health risks of prolonged sitting. wellhealthorganic.com
recommends aiming for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities such as walking, jogging, cycling, or practicing yoga can help counteract the negative effects of prolonged sitting and improve overall health.
Conclusion
Prolonged sitting poses significant health risks, including cardiovascular disease, obesity, musculoskeletal problems, diabetes, and mental health issues. By following the practical tips provided by wellhealthorganic.com
, you can mitigate these hazards and promote better health. Incorporating regular movement, using ergonomic furniture, practicing good posture, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular physical activity are key strategies for leading a healthier and more balanced life. Addressing the risks associated with prolonged sitting is crucial for enhancing overall well-being and reducing the likelihood of chronic health conditions.
FAQs:
1. What are the primary health risks associated with prolonged sitting?
- Prolonged sitting is linked to several health risks, including cardiovascular disease, obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, musculoskeletal problems, and mental health issues. Extended inactivity can lead to higher blood pressure, increased blood sugar levels, excess body fat, poor posture, and reduced mental well-being.
2. How does prolonged sitting affect cardiovascular health?
- According to wellhealthorganic.com, prolonged sitting can contribute to cardiovascular problems by increasing blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and unhealthy cholesterol. These factors can elevate the risk of heart disease and stroke. Sedentary individuals are at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular conditions compared to those who are more active.
3. What steps can be taken to reduce the health risks of prolonged sitting?
- To mitigate the risks of prolonged sitting, you should incorporate regular movement into your routine. This includes standing up and moving every hour, using ergonomic furniture, maintaining good posture, staying hydrated, and engaging in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
4. How does prolonged sitting contribute to obesity and metabolic syndrome?
- Prolonged sitting reduces the body’s ability to burn calories, leading to weight gain. It also contributes to metabolic syndrome, which includes high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, excess abdominal fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels. These factors increase the risk of type 2 diabetes and other chronic diseases.
5. Can prolonged sitting impact mental health?
- Yes, prolonged sitting can negatively affect mental health. wellhealthorganic.comhighlights that sedentary behavior is linked to higher levels of anxiety and depression. Lack of physical activity can decrease the production of mood-enhancing chemicals, leading to a decline in overall mental well-being.
READ MORE :- https://ricepurity.co.uk/well-health-tips-in-hindi-wellhealthorganic/